SEO metrics informs you your SEO effort's performance and success. You can use these metrics to set your objectives and goals. Here are 8 SEO metrics you need to track as a beginner to the SEO world.
If you are starting in the search engine optimization world, well, you are heading in the right direction.
Congratulations!
Now, you will realize that tons of data and numbers can easily overwhelm you in SEO.
But don’t worry, this article will guide you through the most important ones.
SEO metrics are essential statistics that can be utilized to evaluate a SEO strategy’s performance or success.
You can use SEO metrics to set objectives and quantify results.
Let’s delve into each of these key SEO metrics.
This post will tell you what each is about, why they matter, and how to monitor them and make sense of it all.
8 SEO Metrics To Measure
1. Organic Traffic
As you may be already aware, any search engine optimization campaign’s main objective is to direct traffic to your website from organic search.
That said, organic search is absolutely free, making it very important to monitor its performance.
To track how your organic search traffic is doing, follow the following steps.
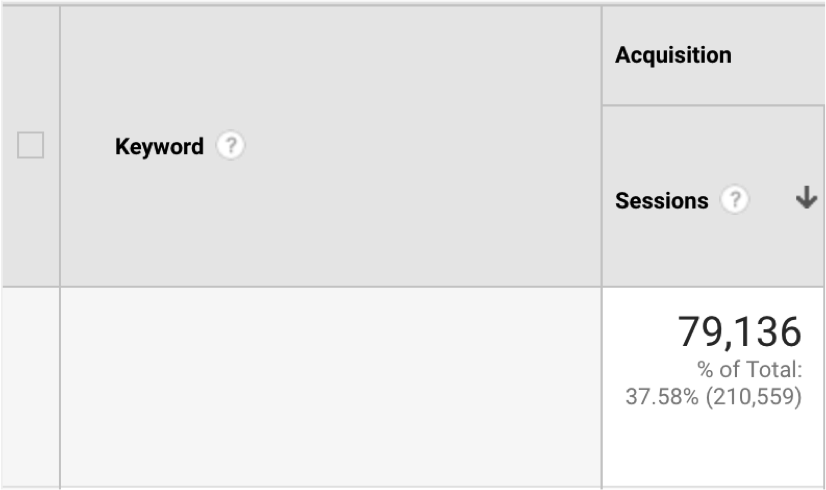
Google Analytics > Acquisition > Channels > Organic Search
You will see a “Sessions” area.
Google defines them as “the number of interactions that take place on your site within a certain time.”
To analyze performance correctly, you will want to look at the periods.
Look at three time frames when measuring any campaign’s success; year over year data, month over month data, and week over week data.
Week over week data
This information helps you see how traffic to your site has adjusted in the short term.
It is essential as it can help you fine-tune your campaigns on the site when making massive changes like installing HTTPS, launching a big content campaign, or setting up 301 redirects.
Month over month data
This is crucial if you want to analyze your SEO efforts’ long-term effects.
Because Google’s ranking factors and algorithms change regularly, just looking at the short-term data can make it a bit challenging to conclude.
Also, SEO is relatively slower than most marketing processes.
So you will want to see the impacts of adjusting the title tag or launching a blog post after a month or so.
Year over year data
This is particularly essential for analyzing your SEO efforts’ long-term effects.
The information is also crucial if your industry or business is affected by seasonality.
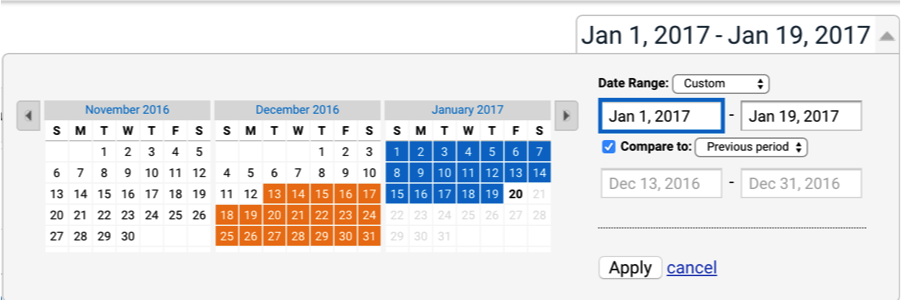
To see this information, navigate the top right corner of your organic search page in Google Analytics and click on the date menu.
Then choose the periods that you want to analyze.
2. Backlinks

Besides relevant and quality content, backlinks are the most vital ranking factors in SEO.
As such, you must track the links pointing to your site.
Here are a few aspects that you should keep in mind:
- The number of backlinks is significant. Though there are cases where a page with fewer backlinks outranks, one with more, if your page has ten backlinks and another has 100 backlinks, the chances of you outranking them are very slim.
- The quality and relevancy of the websites linking to your site matters. If you sell sofas and get backlinks from a site that sells cars, search engines will likely regard these links as spammy and penalize you. The opposite is true if you are getting links from related and relevant industries.
- How diverse the referring domains are also matters. Google looks at how many sites link to you as well as the total number of backlinks. Five thousand links from 500 websites are way better than 1000 links from 2 sites.
And there are many tools online that can help you track referring domains and backlinks.
For example, with Ahrefs, you can easily see all the sites linking to your site, the page they are linking to, and their domain rating.

3. Keyword Search Volume
Keyword search volume is one of the key SEO metrics because keywords with a high search volume usually help drive traffic to a site.
Most people are using it to search for specific products or services.
That said, there are many tools out there that can help you conduct keyword research and then track the search volumes of the keyword you are targeting.
A good example is BiQ’s Keyword Intelligence tool.
It will show you search intent and gather data on keyword volume, trends, keyword competition, and related keywords.
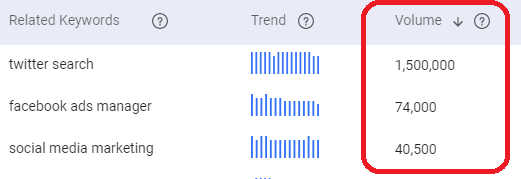
What’s more, the fantastic research tool will show you a list of keywords that local people are using.
For instance, your target keyword search volume can be 500 in a certain location and possibly lower or higher in another.
That is mainly because of the varied needs in different areas.
So, go for a keyword that has a high search volume but low competition.
A high-value keyword means it will bring more traffic to your website at a lower competition.
4. Cost Per Click

One of the few SEO metrics to measure is cost per click or (CPC), which refers to the amount a site owner pays every time a visitor clicks on a paid advert.
CPCs vary by type of business but like click-through’s you will want to track the trends.
While the last five years have seen CPCs increase generally, the surge has been faster in some industries than others.
Similarly, note that CPCs usually depends on how competitive the keywords you are using are.
If the CPCs increase, consider incorporating long-tail keywords to drive more traffic or increasing maximum bids to stay competitive for the most vital keywords.
Also, look at CPCs when defining your maximum budget.
If you have a certain conversion objective in mind.
For instance, let’s say your standard click cost is $1, the conversion rate is 2 %, and you want to convert at least 20 sales every month.
So, your budget per month should be $1000 (1000 clicks by 2 % conversion rate= 20 sales and 1000 clicks by $1=$1000).
Generally, most advertisers prefer using lower CPC to save on their campaigns.
To help you find the right keywords, you can use BiQ’s Keyword Intelligence again.
What makes it unique is its keyword analyzer feature.
It helps users see why some people are searching for a certain word in search engines.
And with this information, you can craft your content in a manner that meets your reader’s needs.
5. Keyword Competition
Most novice content creators select a keyword, create quality content, and then optimize it only to realize that they are not doing well or ranking.
The most common cause of that is stiff keyword competition, aka keyword difficulty.
This is where thorough keyword research to determine difficulty comes in.
By analyzing keyword difficulty:
- You will get a good idea of what the “big players” and “hot keywords” in the industry are.
- You will pinpoint keywords in your industry or niche that you can easily rank for.
- You will save time and money by concentrating only on keyword phrases that bring results even if you don’t have authority.
That said, keyword difficulty is only part of the factors that you should keep in mind when doing keyword research.
The other elements are the relevance and popularity of the keyword.
If a keyword has low difficulty but does not have search volume, you will not get any traffic.
Similarly, if it is not relevant, you will not rank for it even if the difficulty is low because search intent does not match your content.
Nonetheless, keyword difficulty alone should not make you skip some words because they are difficult to rank for.
It is all about having an idea of what you are up against and then coming up with steps to make your site a worthy competitor.
Here are some things you can do to rank for highly competitive keywords:
- Create unique content: You can outrank even an authoritative site with quality and useful content that shows better expertise and covers the topic from a different angle.
- Topic relevance: Developing narrowly oriented content with quality backlinks can help you outrank other sites that cover the subject shallowly and rank only because of their general brand authority.
- Quality backlinks: A considerable number of backlinks to a certain page can help you rank for that topic even if your domain authority is lower.
6. Page Speed

Just like the name suggests, this data evaluates how quickly your website pages load in browsers.
This is important for SEO as well as user experience on mobile devices.
You can check this too in Google Analytics.
Head to:
Behavior > Site Speed > Page Timings
From there, adjust the second column’s numbers to average page load time.
You will see the average load times of all the pages on your site.
You can also use the search bar to check each page’s loading time.
Now, faster load times are ideal for SEO and other factors, so try and make the time as short as possible.
A good place to start is less than 5 seconds and then fine-tune it to 3 seconds with time, particularly for vital pages.
7. Bounce Rate

Bounce rate is defined as the percentage of single-page sessions (i.e., sessions in which the person left your site from the entrance page without interacting with the page).
The bounce rate is one of the most effective ways of determining user engagement on a website.
Low bounce rates essentially indicate that users found your pages interesting or useful.
On the other hand, a high bounce rate shows that users found your page uninteresting or irrelevant.
However, this does not apply to all pages.
On top of the funnel, blog posts can have a high bounce rate because a user’s question was responded to, and they are okay.
This is why it is very important that you set up event tracking to monitor pages’ performance.
That said, if you notice that important pages on your site have a high bounce rate, it is a sign that you should do more on aspects such as content, UX, page speed, and navigation.
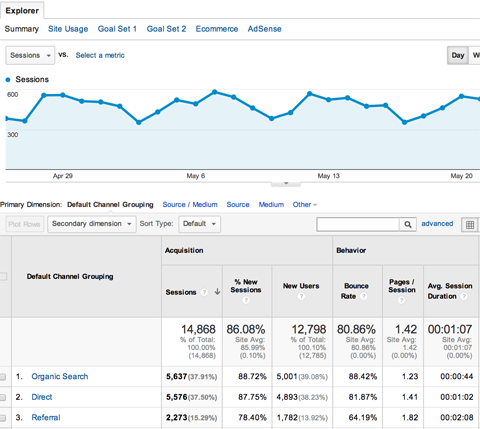
To view your bounce rate, go to:
Acquisition > All Traffic > Channels
The 4th column will show you the general bounce rate for every channel, i.e., paid and organic.
8. Keyword Rankings
Keyword ranking is the position your site is placed in search engine results pages for a specific keyword.
Keyword ranking is the product of your SEO strategy.
It lets you identify which pages of yours are successful in holding those top ranks on the first page and which sites need to be re-optimized.
You can use keyword tracking tools such as BiQ’s Rank Tracking to ascertain the number of keywords that your site ranks for in search engines.
After that, use the information to guide your SEO strategy.
The tool offers a rank tracking feature that helps users fill in the missing data you would otherwise see in your Google Search Console.
All you have to do is create a rank tracking profile for your website, and you can keep track of your keyword’s daily rankings and its historical data.
You will also be able to quickly identify your keywords’ gains or losses so you can act in response to secure your keyword rankings from being stolen by a competitor or take the chance to boost your keyword rankings further while it’s in trend.
Also, take note of the keywords you want to rank for, but you are yet to.
They should be your main focus on SEO efforts.
Another good idea is to take advantage of your current success.
If your site is ranking for high converting phrases, continue utilizing the keywords in your marketing campaigns to make sure you stay there or do better.
The keywords you are ranking for are more likely to drive more people to your site.
So make sure the pages associated with them are relevant and useful to minimize your bounce rate.
Conclusion
While there are other SEO metrics are not mentioned in this list, these ones are the most vital currently.
Use these SEO metrics to monitor the success of your SEO efforts, set KPI objectives to maximize success, and guide your tactical decisions to create more revenue and traffic.
Hopefully, you adopt some if not all of these SEO metrics as KPIs for your next SEO campaign.
Good luck!