Search engine is a web-based tool that helps web users find information stored on the internet. Learn how search engine works and some of Google's ranking factors for ranking a webpage.
Today, Internet users strongly rely on search engines to find information on the web.
They have become powerful tools and an essential part of everyday life.
Search traffic accounted for nearly 30% of total web traffic in 2019. This includes both organic search and paid search, highlighting the importance of these platforms in directing user flow to websites.
Search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo help you find relevant content rapidly.
Ever wondered how search engines work?
Here is an overview that’ll help you in understanding search engines to inform effective SEO strategies.
What is a Search Engine?
Search engine is a web-based tool that helps web users find information stored on the Internet.
They are programs that search web pages or documents based on specific keywords or phrases.
A search engine is a collection of programs.
However, we use the term to describe systems that enable you to search for information on the World Wide Web.
Earlier search engines held indices of a few hundred thousand documents and pages, with a few thousand queries a day.
Today, the major search engines index hundreds of millions of pages, responding to millions of search queries a day.
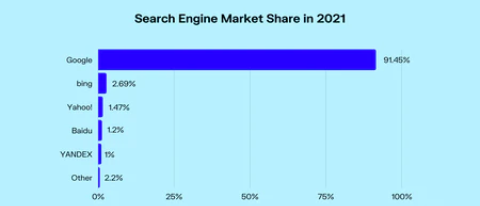
Google is by far the most dominant web search engine today with a global market share of 91%.
Its closest rivals, Bing and Yahoo, command only a fraction of this volume.
How Search Engines Work
Different search engines function in different ways.
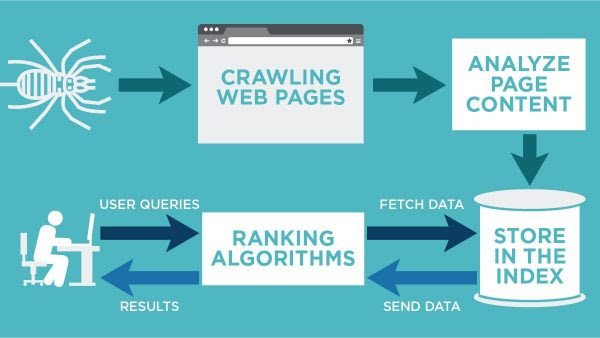
However, all search engines operate in a four-step model:
- Crawling the Internet and following links to find web pages.
- Indexing the web pages to formulate an index from each keyword to every site it occurs.
- Ranking the web pages so the most relevant show up first.
- Displaying the search results such that users can easily understand.
1. Web Crawling

Web crawlers are programs that download web pages associated with the seed URLs.
Web crawlers also extract links in the URLs and proceed to download web pages from identified links in a methodical fashion.
You can refer to web crawlers as web spiders, bots, worms, or ants.
Web crawlers begin with a list of URLs to visit.
These are called seeds.
As a web crawler visits the URLs, it identifies the URL links and includes them in the list of URLs to visit.
This is the crawl frontier or Caffeine in the case of Google.
The crawler then visits URLs from the crawl frontier based on a set of policies.
A web crawler is a vital part of a web search engine since it uses the program to collect tons of web pages that it indexes.
Web crawling enables the search engine to search faster and more efficiently.
The amount of data a search engine can retrieve for results determines the data a search engine can store.
Google is able to index around 3 billion web documents, far more than any other search engine.
2. Web Indexing
An index is a point-out or guide that facilitates reference.
Web indexing is one of the most important information retrieval tools.
A web index is a compilation of terms with pointers to sites or documents where you can find information.
Most search engines used automatically generated indices, either in combination with different technologies or by themselves.
Web indexing utilizes interdisciplinary concepts from computer science, mathematics, linguistics, or informatics.
The major search engines focus on indexing full-text natural language documents online and media types.
Indexing optimizes the performance and speed in finding documents for a search query.
Without an index, search engines would take considerable amounts of time retrieving information on the web.
3. Search Engine Ranking
Search for anything using your favorite search engine.
Almost instantly, the search engine will sort through millions of pages it has indexed and display the pages that match your search query.
The search engine often ranks these pages such that the most relevant results show up first on the list.
Search engine ranking is the process or criteria via which a search engine orders these results to satisfy your search intent.
Generally, highly ranked web pages contain more relevant information to your search query than lowly ranked pages.
Most search engine search results are text-based.
They will display results from queries as a list of pointers.
The lists sometimes have or lack summaries of the retrieved web pages.
What is a Search Engine Algorithm?
A search engine algorithm refers to a unique set of rules that search engines employ to rank page listings in response to your search query.
Search engines send a crawler through the site periodically to analyze all its data.
The crawler analyses the data and uses the search engine algorithm to value web pages and determine their relevance and ranking for various searches.
Search engine algorithms are rather complex and are closely guarded trade secrets.
They are unique to the search engine and determine search engine result pages (SERPs).
For instance, Google alone employs more than 100 variables in their search algorithm.
How Does Google Search Algorithm Work?
At the heart of Google’s Search engine is its search algorithm or PageRank algorithm.
Google search algorithm assigns each web page a rating based on its importance.
Google uses various factors to determine the relevance of a web page to the search query.
Google looks at various factors that affect each other.
The relationship between each factors shift constantly.
Let’s say you searched “spicy chicken recipes.”
Google’s algorithm will weigh the web pages against your search term.
The first factor is the URL.
Keywords may show up in the URL, such as www.recipes.com/spicy-chicken.
Google can see the keywords “recipes” and “spicy chicken,” so it can apply an appropriate weight.
Now to the second metric, which is backlinks.
Many of the backlinks may contain the keywords in them.
Now Google can down-weigh this factor since you expect keywords in the URL to appear in the backlinks (whether they are relevant or not).
On the other hand, if the keywords don’t appear in the URL, Google may choose to apply more weight to the second metric.
Google releases hundreds of algorithm update every year.
The relationships between metrics shift more than the metrics themselves.
When the metrics themselves change, it’s often a major algorithm update such as Panda or Penguin.
Google Search Engine Ranking Factors
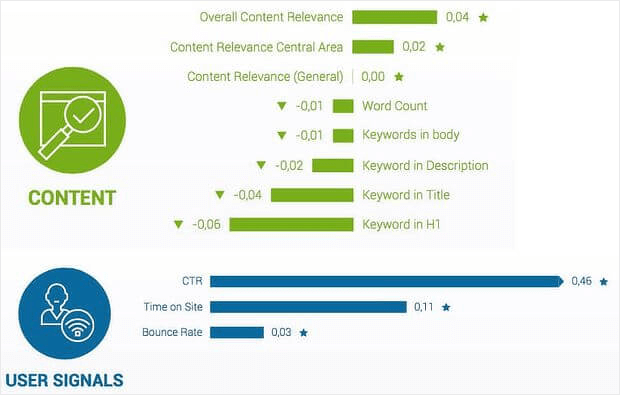
1. Relevance
How relevant is the web content to a user’s search query?
Google’s indexer is the first test on relevance.
It determines if a web page should appear in the SERPs at all.
When you are searching for something online, you want to view the most relevant results possible.
The better the content or text on a web page matches a query, the more likely the page is to rank higher.
Google determines relevance based on a mix of on-page and off-page factors.
These include visible text, videos, images, and meta elements, including title, anchor text, alt tags, and meta descriptions.
The most basic signal of relevance is if a web page has the keyword in the search query.
Google also employs anonymized and aggregated interaction data to determine if results are relevant to queries.
Google transforms this data into signals to help their systems estimate relevance more effectively.
2. Freshness

Content freshness is an important Google ranking factor today for specific content.
Fresh content is essentially timely or new content.
Google employs Query Deserves Freshness (QDF) to weigh content freshness.
Content freshness is closely tied with content relevance.
QDF determines the weight of freshness in Google rankings.
This means that not all queries will be subjected to freshness as a ranking metric.
For users that search for content that requires updated information (events), the content has to be fresh to stay relevant.
Google focuses on the user.
If it doesn’t make sense to the query, it doesn’t need to rank.
Metrics that impact freshness include:
- Inception date
- Core content changes
- Percentage of change
- Frequency of change
- Amount of new content
- Link growth rate
- Anchor text changes
- Traffic and engagement signals
A great asset that you can use to come up with fresh content ideas is the Keyword Intelligence feature from the BiQ AI-based SEO suite.
You input your keywords, and BiQ creates a list of content ideas you can follow.
The tool also displays crucial metrics that can help you select a topic.
The search volume feature displays the demand for a particular topic.
The trends feature informs you if a topic is emergent to capitalize on engagement.
3. Search Intent
Search intent or user intent is the main goal of a web user when searching a query using a search engine.
Often, lots of users are looking for specific types of content or resources.
Search intent is important to Google, as its primary goal is satisfying user intent.
Let’s say you search for “How to repair a refrigerator.”
If you’re shown product pages for buying refrigerators, you’ll try another search.
This will signal Google that the intent of the results doesn’t match your search intent.
On-page SEO is vital for satisfying user intent, and BiQ Keyword Intelligence tool can help you in this regard.
This tool helps you predict the intention behind keywords using a rule-based AI algorithm.
BiQ Keyword Intelligence classified your keyword intent as transactional, navigational, or informational.
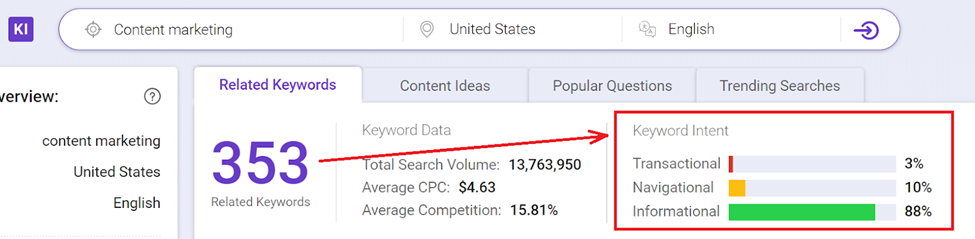
This analysis can help inform your content creation strategy through an understanding of your target audience.
4. Content Quality
Content quality is among the most important ranking factors.
Beyond matching keywords with relevant pages on the web, Google looks to prioritize the most reliable sources.
Google has designed its systems to identify signals that help determine the web pages that demonstrate authoritativeness, expertise, and trustworthiness on the given topic.
Google looks for websites that many searchers tend to value for similar queries.
Google will reserve the top rankings for websites with well-researched, well-crafted, and in-depth content that satisfies search intent.
Google’s webmaster guidelines detail the characteristics that define low-quality content.
Search Engine Optimization
Now that you understand how search engines work, you have to optimize your webpages such that they rank higher in SERPs and increase your online visibility.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the collection of techniques you use to help your web pages rank higher in natural (organic) search results.
There are two categories of SEO; on-page and off-page SEO.
1. On-Page SEO

On-page SEO entails all aspects you can control on your web pages and across your site to ensure search engines find, index, and rank your content.
Below are the key elements of on-page SEO:
- Website Content – Your content has to be relevant, useful, and engaging to your target audience. Formatting also impacts how search bots digest your web content. Your content should have an attention-grabbing headline and include keywords you seek to rank for.
- Keyword Research – Keyword research is the cornerstone of SEO and helps you understand what your audience wants to find. Keyword research also helps you discover new keywords and search volume. You can use Google Keyword Planner in this regard.
- URL structure – An organized URL structure ensures search engines can easily index and understand your site content.
- Title Tags and Meta Tags – Title tag is the text snippet appearing in the web browser’s upper left corner. Good SEO practice is including your keywords in your title tags. Meta tags are code snippets you include in a page’s HTML and include meta description and meta keywords. Search engines will look for meta descriptions to find the text to display under your title tag.
- Image Optimization– images are crucial components of any website. However, poor optimization can lead to slow speeds. Ensure that you compress your images.
- Internet Linking – The crawlability of your site partly lies in your linking structure. Search engine crawlers can find all your pages when you link them to other pages and help users navigate your website.
2. Off-Page SEO

Off-page SEO encompasses aspects that happen off-site to help build quality backlinks.
It can be more difficult to execute compared to on-page SEO.
The main components of off-page SEO include:
- Link building
- Social media marketing
- Email marketing
- Local SEO
Measuring and Optimizing SEO Success
Effective SEO is a long-term process.
It’s equally important to pay attention to metrics used in measuring performance.
Measuring performance help identify key areas that you need to improve on and areas to direct more resources.
There are numerous metrics or KPIs that you can track daily, weekly or monthly to inform your SEO strategy.

These metrics include:
- Web traffic
- Leads/ROI
- Click-through rates
- Conversion rates
- Dwell time on page
- Bounce rate
- Impressions volume
Conclusion
Overall, search engines are a crucial component of any web-based venture today.
Understanding search engines and how they work help you optimize your content for improved rankings.
Proper search engine optimization will help improve your online visibility and increase traffic as you add value for your users.