Choosing the wrong redirect may cause SEO issues that can go unnoticed for long periods of time. This post will explain the difference between 301 and 302 redirects and when to use them correctly.
Redirects are really simple to understand.
If you’re moving your website content to a new location permanently, you’ll need to use a 301 redirect.
But if you’re only moving it temporarily, then use a 302 redirect.
Unfortunately, not many people know why this is important.
After all, online users can’t always tell whether you’re using a 301 or 302 redirect.
Both are somewhat identical in their functionality.
The simple answer to your question: search engines view 301 and 302 redirects differently.
Therefore, choosing the wrong redirect could cause several SEO issues.
And the worst part is that most of these issues could go unnoticed for several months or years.
The 301 vs 302 redirects issue has been an on-going debate for several years now.
But this post will clarify the difference between 301 and 302 redirects and put the uncertainty to bed.
What is 301 Redirect?

A 301 redirect is the status code the server sends to your visitor’s browser.
It’s one of the many possible status codes used by servers.
You’ve probably seen or heard of it when browsing the internet.
When you visit a web page, and the server finds that page normally, it sends a 200 – OK status code.
However, if the website requested by the browser redirects it to another website, it sends the 301-redirect status code.
Once you move a piece of content from a specific website URL, browsers that try to visit it will receive the 404 – page not found status code.
This can be very depressing, especially if the visitor really needed to check out that specific page.

To improve your visitor’s journey, you will ask the server to send the 301 – Permanently Moves status code instead, then move the visitor to the new web page where they’ll find the content they were initially searching for.
These processes happen so quickly that users usually aren’t even aware of them.
You simply find the content you requested in front of your screen.
The keener users will notice the change in URL name.
It won’t be the same as what you initially typed and clicked.
Essentially, 301 redirects let search engines know,
“Hi, you know that content piece that people used to enjoy clicking on from the SERPs? It lives over here now. So, kindly take all that visibility and page rank associated with it, and transfer it here, to this new URL.”
That’s why 301 redirects are crucial for SEO.
When to Use 301 Redirect
Here are other great use cases where 301 redirects would apply as an excellent tool.
Permanently Changing a Site’s URL
You already have an idea of what we mean by this.
It’s all we’ve talked about when mentioning 301 redirects in this post.
So, maybe your initial URL was poorly optimized, or you’re re-organizing your website’s folder structure.
Moving a piece of content from one URL to another isn’t a difficult task.
You simply change the URL on the settings tab of your content’s edit page.
Your CMS will automatically add the new URL redirect from the original web page to the new one.
Ensure you check that the new URL is working before moving on.
Moving to a New Domain Permanently
You can also use a 301 redirect to relocate your web content from one domain to another permanently.
It’s vitally important that you implement 301 page-to-page redirects from the old domain to the new one.

This process is relatively easy if the website is moving a domain but maintains its structure and layout.
It’s particularly efficient if you’re looking to change or restructure content.
However, you must take care to make the redirection sensible for the search engine and user.
It must honor your users’ original intent.
Only then can you pass your content visibility and page rank from your old pages to their new counterparts.
When implementing a page-to-page 301 redirect, you must remember to serve the redirects from the original URL.
Changing from HTTP to HTTPS

While many websites still run the HTTP security protocol, a significant portion has converted to the more secure HTTPS.
The sites still using HTTP connections pose the risk of exposing users’ personal information when using the site.
Third parties could intercept your personal data and use it for some illegal acts.
Thus, the main reason why Google is pressing websites to change to HTTPS connections.
However, that’s easier said than done.
If you’re planning to move an entire website from HTTP to HTTPS, you must be very careful as even the slightest mistake could break your web links.
This can negatively affect the transition process, which will impact your website’s visibility and overall rank.
By proper relocation, we mean setting up a 302 redirect from every HTTP web URL to its HTTPS counterpart.
Merging Two or More Web Pages
If you’ve got multiple content pieces that overlap each other, thereby cover the same topic or compete for the same keyword, you may want to consider consolidating them.
Then again, you wouldn’t want to throw away the visibility some of your old web pages might have achieved in the search engine.
After creating a new page with the consolidated content, you must remember to set up a 301 redirect from each of your old web pages to the single new one.
BiQ Content Intelligence is a particularly helpful tool here.
The Content Intelligence tool will provide you with relevant insights to analyze and optimize your content post-publishing.
This way, you’ll have a second chance to make your consolidated content even more attractive and appealing to both the search engine and users.
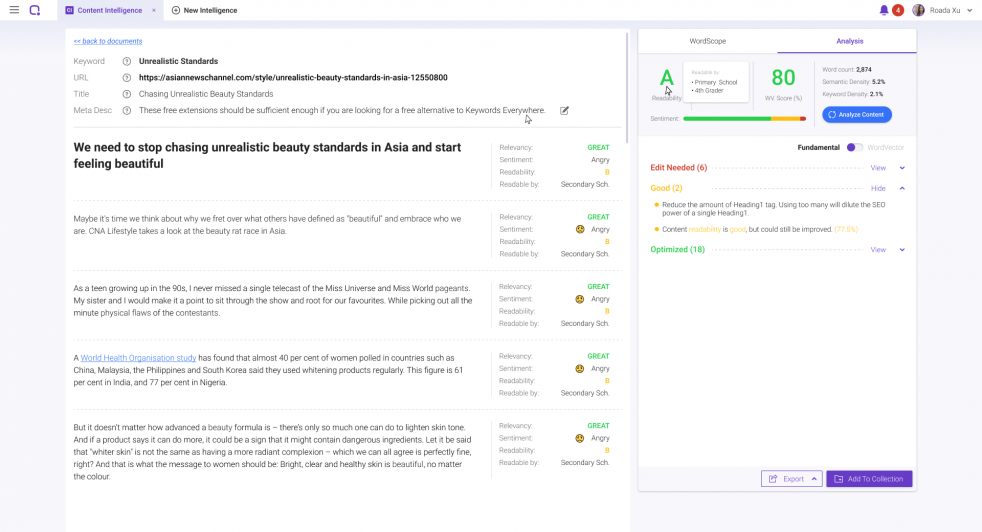
Using the BiQ Content Intelligence feature guarantees you a full analysis of your content and provides you with three critical data to ensure you publish only A-grade content.
These include:
- Paragraph by paragraph analysis
- Overview of your content performance
- Check the WordVector and other fundamental SEO optimization processes
These critical insights will help you optimize your content further and improve your content ranking and visibility for the new web page.
What is 302 Redirect?

In the 301 vs 302 redirects battle, the 302 redirect is often used less often.
At its core, this redirect tells the search engine and users that the page they are searching for has been moved to a new URL (temporarily).
Remember the word temporarily when using 302 redirects.
It means the web page has moved to a new page only for a short period.
Unlike the 301 redirect, the 302 redirect does not pass most of its qualities to the new redirected web page.
This is where the main difference between 301 and 302 redirects arises.
With 302 redirects, the original web page maintains its Google ranking.
Therefore, it shouldn’t affect your SEO efforts.
The redirected page will still maintain its page authority, page rank, and traffic value.
It’s also worth noting that the detour URL won’t accumulate any of the qualities mentioned above.
This is quite a dangerous gamble, especially if you use a 302 redirect by mistake.
If you use a 302 redirect, Google will know your page is coming back.
When to Use 302 Redirect
If you’re moving your web page to a new location for a short period, you will want to use the 302 redirect.
Doing this will preserve your original pages’ integrity (and rankings).
Here are a few examples of when to use the 302 redirect.
Performing an A/B Test of a Page
Whether you’re in the service industry, eCommerce industry, or running a local business, performing an A/B test is crucial for your overall bottom line.
An A/B test allows you to test different versions of similar pages of your website to determine which version drives more sales, conversions, and other behaviors users take.
Well, you wouldn’t want to redirect to the new web page permanently.
You never know.
You might realize later that the original page was actually better.
That’s why we recommend you use the 302 redirect.
This will temporarily send a portion of your web visitors to the adjusted web page without losing your rankings.
After finishing the test, remove the redirect.
When You Have a Broken Web Page, and You Want to Maintain User Experience
Another great instance where a 302 redirect applies is when a web page is broken or inactive.
You’ll not want your visitors to land on a blank web page.
In such instances, a temporary redirect is the way to go.
Remember, you should only use the 302 redirect when you plan to bring that page back.
A 302 should ensure your website maintains its SEO ranking and ready to go whenever you plan to reactivate it.
Obtaining Feedback on Your Old Page Without Affecting Its Ranking
When your client requests feedback on a specific feature or design on your website, you can actually show off how they work without worrying about users visiting your website.
A 302 redirect allows you to obtain feedback on your old web URLs without affecting your SERPs.
Running Time-Sensitive Maintenance and Want to Redirect Visitors to a Page for a Short Time
If your page is under development or maintenance, you’ll probably need to use a temporary redirect.
Other more extensive redesigns may require taking your website offline.
This can frustrate users and even confuse the search engines.
Instead of leaving your web visitors hanging, you should apply a 302 to let them know that your web page is down temporarily and will be back soon.
In such instances, you may send your visitors to a sign-up page or display a countdown clock informing them when your website will be back.
Check out this countdown page with a countdown clock.

Additionally, it’s essential to add links to your social media accounts to build and improve your social media presence.
Which Affects Your SEO: 301 Vs 302 Redirects

As you’re very much aware by this stage, a 301 means a permanent relocation of your web page URL, while a 302 means a temporary relocation of your URL.
That said, it’s worth noting that every time you move a web page from one URL to the other, it takes search engines a while to notice the change.
Only then will you see any real impact or change to your page rankings.
When used correctly, a 302 redirect won’t hurt your SEO efforts.
Therefore, your original page will remain indexed in Google.
No value will be transferred to your new URL since Google will know it’s just temporary.
You’ll retain all rankings, page authority, and traffic value the old page might have.
When it comes to 301 vs 302 redirects, the debate arises from not knowing the difference between the two or which ones to use.
What’s important is understanding the difference between 301 and 302 redirects and the best time to use either option.
Therefore, you cannot afford to mix up how you use either redirect.
However, if Google realizes that you actually used a 302 redirect when you initially intended to use a 301 redirect, the search engine giant will reindex your new website URL instead.
But you must also remember that Google doesn’t always catch these simple mistakes.
The search engine can also reindex your 302 to a 301 if it notices that your temporary web page has been up for too long.
It may assume that you meant to use the 301 redirect instead of the 302. Thus, the reason to make haste and not to leave the 302 redirect up for too long.
Conclusion
Redirects aren’t complicated.
It’s just a matter of knowing which redirect to use, and where.
If you’re relocating your URL to a new location permanently, ensure you use the 301 redirect.
However, if you’re relocating your content temporarily, then use the 302 redirect.
These two redirects can get really confusing, and navigating them can be a pain, especially if you’re not a technical SEO expert or developer.
Knowing the difference between 301 and 302 redirects can also make a big difference in your SEO efforts.
Now that you understand these two redirects and know where to use them, ensure you implement each one the right way on your website.