With duplicate content, site owners may suffer from traffic and ranking losses or risk getting penalized. Here's how duplicate content affects SEO and how to fix them.
Duplicate Content and SEO: Deal with It Or Live with It?
Melania Trump copied Michelle Obama’s previous speech in the 2016 Republican National Convention, word for word. The world laughed.
The same thing happens online every day.
30% of all web content is duplicate content, according to Matt Cutts, former Chief of Search at Google. Duplicate content is a term for content that appears in more than one URL on the same domain or other domains.
Beware, duplicate content is an SEO black hole. It sucks all your ranking potential and ultimately renders you non-existent in the digital sphere.
Duplicate content should be fixed ASAP because:
- It is spamming users
- It is tricking Google search bots (they interpret it as so)
- It is compromising your credibility
What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content refers to indistinguishable or fundamentally the same content showing up on more than one site page, within or outside your site.

Matching content is viewed as risky for SEO because search engine bots categorically avoid showing web pages with the same content in SERPS.
Other ways to define duplicate content
- Copied content
- Affiliate content with no additional value
- Shared or syndicated content with no links to the source
How Does Duplicate Content Affect SEO?
1. Reduced organic traffic
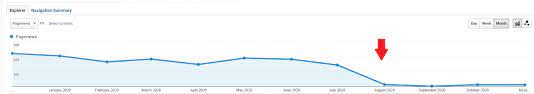
Google does not like to rank pages that use the same content replicated from different pages in its index, even if those pages are on your website.
Suppose that you have three pages on your site with the same content. Google won’t be sure which page is the “first.” So, every one of the three pages will be fighting for ranking potential.
Look at this example of duplicate content titled ‘blog’ appearing at three URLs:
- www.http.domain.com/blog/
- www.http.domain.com/blog/?utm_content=buffer&utm_medium=social
- www.http.domain.com/classification/blog/
The first should appear in SERPs, but Google will fail to understand the situation and might instead the second –an undesirable URL– in search results. This reduces organic traffic.
2. Duplicate content penalty can occur
Google has said that duplicate content doesn’t prompt a punishment. Even so, there are times when the search engine giant penalizes brands for what they call “intentionally manipulative duplicate content.”
This refers to the uncommon cases where Google perceives that duplicate content is created to control rankings and dupe searchers. The punishment for that is lowered ranking or de-indexing of the involved websites. If your site is taken from Google Indexes, it won’t show up in search results.
Sites that are more likely to face this kind of punishment include:
- Sites with many different pages,
- Domains or subdomains with loads of similar content.
- Pages where 70% of the content is copied from other domains
- Using affiliate content or product pages with no unique value to searchers
3. Fewer indexed pages
This is particularly significant for sites with collections of pages. If your eCommerce website has a lot of similar content on each page, Google may downrank the site or refuse to rank the pages altogether.
Google doesn’t index pages with duplicate content. If you have pages that aren’t getting indexed, it very well, maybe because your SEO is wasted by duplicate content.
4. Bad for user experience

When a user access content on your pages, they expect material that is unique and fresh. But if they come across the same content on every page, it diminishes the chances of finding the answers to their questions. This reduces credibility for you.
Google finds new material on your site through crawling, which implies they follow links from existing pages to new pages.
Having duplicate content reduces crawl efficiency. Together with de-indexing, this can reduce the speed and recurrence at which they crawl your old and new pages. When a user specifically searches for content on your pages, the search engine may delay showing results. In a nutshell, fewer bots crawl your site if it’s established that content is duplicate.
Internal vs External Duplicate Content
(i) Internal duplicate content:
Internal duplicate is when the same content exists in more than one URL on your website.
The most at-risk sites are eCommerce websites or site administrators that use similar headings and meta-descriptions in their pages.
(ii) External duplicate content:
External duplicate content is when the same content appears on other websites and their pages.
The most at-risk websites include news sites and brands with niggardly content budgets.
How Duplicate Content Occurs
In most cases, website administrators don’t purposefully make duplicate content. However, that doesn’t mean that duplication is non-existent. 20- 30% of web content is duplicate content, and it mostly arises from these causes:
1. Indexing
Sometimes pages get indexed automatically. On Google Search Console, if you find that your website has more pages indexed than the number of pages currently on your site, that possibly means that the pages are replicated.
2. Tracking parameters
Most internal duplicate content arises from URL parameters when the parameters appear in the URL itself.
Most websites use URL parameters for different URL variations. The result is that search engines index separate versions of the same URLs, including the parameters.
For instance:
www.eurodecore.com/dec-decorations
is a copy of
www.eurodecore.com/dec-decorations?source=rss
These are different URLs, but they do not change the content of the page—December decorations. Although the latter has a tracker that allows you to identify the source of traffic, it eats into the canonical URL’s ranking potential.
3. Session IDs
Duplicate content can also arise out of session IDs. This happens when every client that visits a site is served an alternate session ID that is put away in the URL.
A session ID helps keep track of visitors on a site and empowers them to fill forms over many days or store items in a shopping cart. An alternative to storing this information is using cookies, but search engines don’t do that. Instead, every new link on the site gets a new session ID included in the URL—this creates a unique URL every time it happens, leading to duplicate content.
4. Trailing slashes vs. non-trailing slashes
A trailing slash (/) after a URL means that the URL is a folder or directory. A URL with a non-trailing slash indicates that the URL is a file.
However, many WordPress sites with folders still serve the same content as those without. That happens regardless of whether the URL has a trailing slash or not. As in the example below, the two URLs below serve the same content:
https://www.duplicatecontent.com/category/trailing-slash/
https://www.duplicatecontent.com/category/trailing-slash
5. HTTP versus HTTPS or WWW versus non-WWW pages

If your site has different variants at “www.site.com” and “site.com” (and similar content at the two locations), you’ve then made copies of every one of those pages.
The equivalent applies to sites that keep variants at both http://and https://. If the two renditions of a page are live and obvious to web indexes, you may run into a copy content issue.
6. Scraped or copied content
Content material includes blogs, videos, articles, and additionally infographic pages. If someone republishes your blog content on their website and fails to link back to your site, that leads to duplicate content online. Both you and the person copying may be penalized.

If various sites sell similar things and rely on the same product descriptions, this can also lead to vast volumes of massively duplicate content.
7. Paginated Comments
WordPress allows for the creation of paginated comments. These create multiple versions of a single URL and can lead to duplicate content.
– example.com/blog/
– example.com/blog/comment-page-2
– example.com/blogt/comment-page-3
8. Localization and hreflang
If you provide similar content to audiences in different locales who speak the same language, that causes duplicate content.
An example is having different versions of your site for AU and US customers. They all speak English, except for different currencies; much of the content will be interpreted similarly.
Forbes expounds more on this rookie mistake.
The Hreflang tag commands Google to show the content in specific pages instead of standard pages based on the language or region a user is searching from. This is another form of language targeting that can produce duplicate content.
Ways To Remove Duplicate Content
Fixing copied content issues involves finding duplicate copies and specifying the original ones.
When the content on a site can be found at numerous URLs, it should be canonicalized for web crawlers. Let’s explore the fundamental approaches to do this:
1) 301 Redirects
Much of the time, the ideal method to remove duplicate content is to set up a 301 redirect from the other pages to the original content page.
Because when different pages with the possibility to rank well are consolidated into a solitary page, they don’t just stop competing with each other. They become more relevant and more popular. This can increase the ranking potential.

2) Rel=canonical tag
Another alternative foolproof technique for dealing with duplicate content is using the rel=canonical tag. This tells web crawlers that a given page should be treated as a duplicate of a specified original URL. The entirety of the connections, content measurements, and ranking potential that search bots apply to this page will be directed to the original URL.
The rel=”canonical” is part of the HTML top of a page and appears as below:
<head>…[other code in document HTML head] …<link href=”URL of original page ” rel=”canonical” />…[other code in document HTML head]…</head>
Add the rel=canonical tag to every page’s HTML head with duplicate content with a link to the original page.

The Rel=canonical tag is as effective as 301 redirects and is easier to implement.
Rel=canonical tag is useful for managing duplicate content on product pages.
3) Robots Meta Noindex, Follow Tag
You can effectively deal with duplicate content by leveraging meta robots when utilized with the qualities “noindex, follow.”
This is also known as the Meta Noindex, Follow or content= “noindex, follow.” You can add this meta robots tag to every individual page’s HTML head for pages that you don’t want e indexed.
Code example:
<head>…[other code in document HTML head]..< meta name=”robots” content=”noindex,follow”>…[other code in document HTML head]… </head>
Search engines will be able to follow the links on a page, but they won’t index those links. The page with duplicate content can, in any case, be crawled, even though you’re instructing Google not to index it.
This approach is the most preferred because Google categorically warns against restricting access to crawlers on your site.
Robots Meta Noindex, Follow Tag is specifically an effective solution for duplicate content created by comment pagination.
4) Internal link consistency
Maintain consistent internal links on the site. For instance, if a website admin determines that the standard rendition of the domain is www.example.com/, at that point, all internal links should follow the same https://www.example.co… instead of http://example.com/bots… (HTTPS vs. HTTP)
When publishing syndicated content, ensure the partnering site links back to the first original page instead of a new page URL.
For further protection against content thieves, add a self-referential rel=canonical connection to your current pages. This is a standard characteristic that focuses on the URL of your existing pages. When the person publishes the content that they copied from your website, the self-referential rel=canonical tag will guarantee your site gets credit as the original source of the content.
Additional Methods for Managing Duplicate Content
* Create NEW content
Create new content for each page, either from scratch or as an update of the available matching elements. Add something new, differentiating, and valuable to users.
Wondering where or how to start?
Use BiQ’s Keyword Intelligence tool to generate new content ideas easily. The SEO solution helps you quickly find topics for blog posts with the highest-ranking potential.
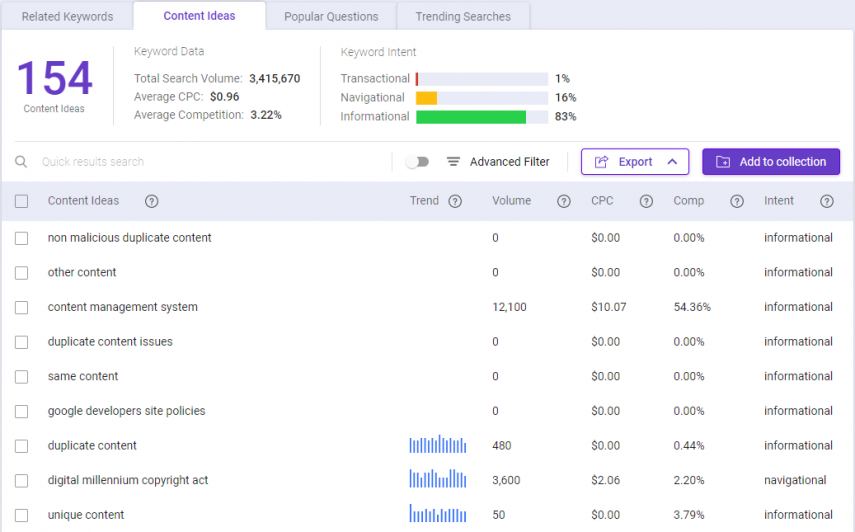
In the Content Ideas section, enter your target keywords or phrases, and the solution will show an extensive list of content ideas to explore.
Let’s say your article about ‘Research X’ appears at http://www.example.com/Research-X/, and the same content also appears at http://www.example.com/article-category/Research-X/.
You can use new content ideas to restructure the 2nd page and 3rd page.
That includes using new titles, new meta descriptions, and further information in the article’s body.
* Create BETTER content
Even paraphrased content often gets flagged as duplicated content. Reposting guest posts falls in the same category too. You can avoid falling into these traps by using the BiQ Content Intelligence tool.
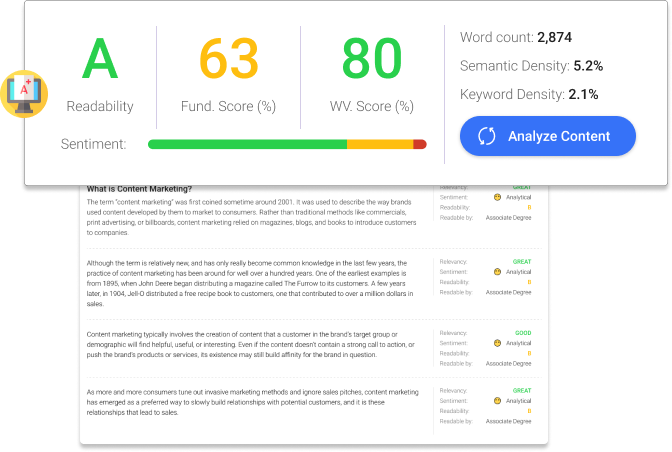
This is real-time support and assistance in content creation. An interactive writing assistant in the edit box helps you optimize your pros with the right keywords and phrases for SEO and originality.
Sign up for a free BiQ account and try out Content Intelligence today!
Conclusion
Duplicate content reduces your ranking potential. It leads to a second-rate user experience on your site. Causes of duplicate content include inconsistency in URLs and internal linking, comment pagination, and tracking parameters, among others.
You can fix duplicate content using 301 redirects or Rel=canonical tag, formatting links consistently, and creating new content.