Google PageRank was the metric used to determine how authoritative your site was. Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin developed PageRank which was the core pillar of the Google search engine.
There are currently 1.72 billion websites on the internet based on data by Statista.
In this clustered digital galaxy, SEO ranking is hugely crucial for business.
SEO ranking is the unbiased positioning of websites on search engine results.
Those on the top spot are the sites that provide the most credible, useful, and relevant answers to a user’s search query.
SEO experts would try to improve page ranking as SEO ranking ensures that users get the most accurate and reliable results for their internet searches.
For businesses, the value of SEO ranking is priceless.
Ranking on top of organic search results means more brand visibility, more site traffic, and better chances of increased conversions.
By improving SEO ranking, you automatically improve user experience and build brand loyalty.
In the 2000s, Google PageRank was the measurement used to monitor page rankings, most notably by seeing the PageRank score.
This PageRank score was significant in determining how authoritative your site was.
Google PageRank History
It all started with WWW on Dec. 20th, 1990.
Soon countless computers and servers would be interconnected, forming what we know today as the internet.
The “jumbled mess” of networked computers birthed the need for a directory, a way of finding information stored on servers and devices around the world.
The “directory” was the browser, and Yahoo was the first in 1994.
It wasn’t until 1998 that Google entered the scene.
They entered with a bang, bringing what was then cutting-edge search technology — PageRank.
In retrospect, this was no more than a link evaluation technology.
Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin developed PageRank in 1996.
Google PageRank algorithm was, in fact, Google Search.
When the prototype was released in 1998, PageRank became the foundational pillar of the Google search engine.
Google PageRank went into work on September 1, 1998, when Google company started operations.
The patent documents reveal that PageRank was a simple but novel algorithm used to quantify a web page’s value and rank it among others on the web.

However, a previous search engine technology called RankDex (present-day Baidu) used hyperlinks just as Google.
PageRank proved to be more effective at sorting out the chaotic material on the worldwide web.
In short, Google was founded on PageRank, an idea that webpages on the web could be ranked based on link prominence and popularity.
A website with more hyperlinks was voted and thus ranked as being the most popular.
The more the links, the higher the ranking.
How Does Google PageRank Work?
PageRank estimated the value of each page and gave each page a score from 0 to 10 to reflect its importance.
0 was the lowest score and ten the highest.
Google simply relied on counting links as a formula for measuring the value and authority of each page.
When a page got a link, Google PageRank considered the link to be a vote of support.
Even so, as revealed in the patent, Google PageRank worked a bit more intelligently by not counting links equally.
The source of those links mattered.
A site that got a link from PageRank 10 was voted as more popular and ranked higher than a site that got a link from Page Rank 2.
Factors That Influence Google PageRank
Today, factors that influence Google PageRank are continually changing and advancing.
But from the early days, Google has always depended on the interconnection of millions of websites on the web.
In truth, websites, links, and consumers made Google number one via PageRank.
But for these consumers, individual sites and links to become number one on Google, the below parametrics must apply:
Anchor texts
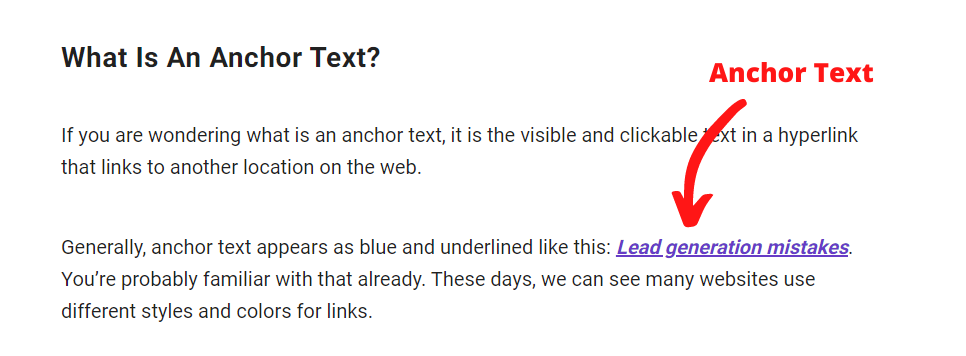
Anchor text is the interactive content in a hyperlink that links to another page on the web.
In the early days, anchor text was one of the primary influencers of a page’s position in Google.
Search engines often pay closer attention to the distinctive anchor text varieties utilized to link back to the first article.
They use these texts as indicators of the article topic and its relevance to a user’s search query.
In 2021 Google PageRank, though secreted away in Google’s dark corners, is super advanced.
In addition to natural language processing, the search engine considers link source and anchor text as some of the most critical influencers of link relevancy scores.
Today, you must put in extra effort when creating anchor texts for your links.
PageRank looks at keywords.
They should be relevant and not stuffed. Keep it basic and ensure the sentence containing the link reads naturally.
Do not use the anchor text that contains precisely the same words as the URL of the link.
You can use the BiQ Keyword Intelligence tool to find related watchwords.
This helps avoid keyword stuffing in the anchor text.
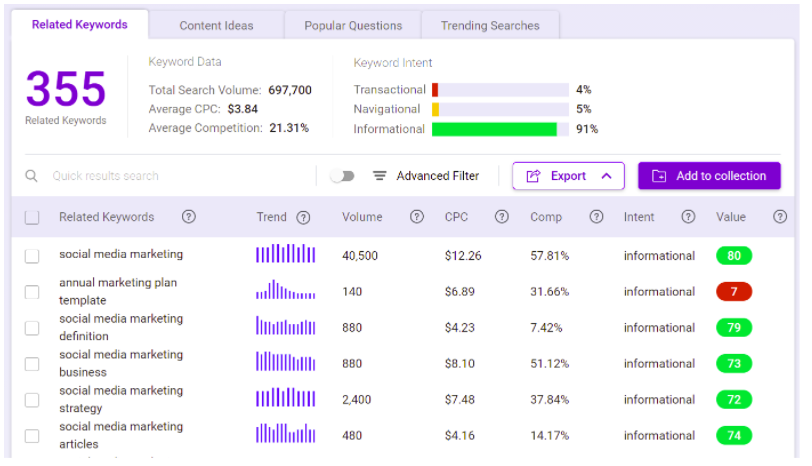
Simply type in the search box your primary keyword and hit enter.
The keyword solution gives a comprehensive list of related keywords, with metrics such as popularity and search intent.
This helps you choose the anchor text keyword with the highest SEO ranking potential.
If you are uncertain which keyword to use, you can choose from among the list based on metrics such as value.
The higher the value, the more the traffic potential of the given keyword.
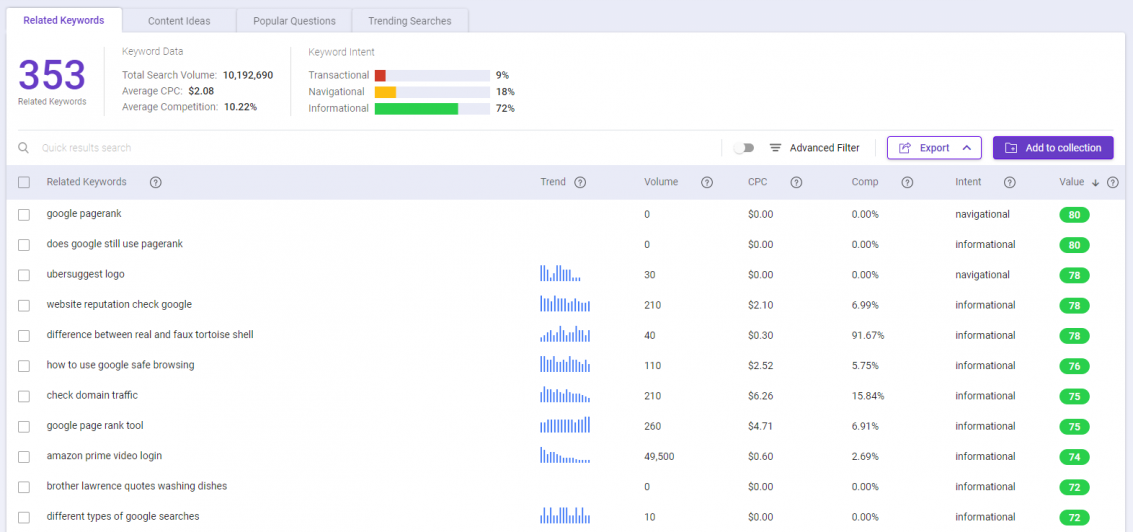
Remember to combine short-form and long-form keywords in your anchor text.
After being duped thousands of times in the 2000s, PageRank is much smarter today.
Having all the links with the same short anchor texts can immediately get flagged as suspicious “black hat” activity.
Internal links
Were internal links significant to Google PageRank?
Do they still matter?
Yes, and yes.
Google PageRank was in the business of ranking pages and not entire websites.
The link authority votes, as seen earlier, were for individual pages. Internal links played a role in this voting too.
They still do.
Without internal links, your ranking potential would be virtually non-existent.
With a robust on-site linking system, you can show Google which content is connected and which of your articles are the most enlightening and important.
Internal linking helps both Google and your clients to understand your site better.
This increases your possibility of a higher SEO ranking.
Internal linking builds up site design and spreads the link votes to other pages.
This linking strategy can help you improve page authority, relevance, client experience, and possibly your rankings.
Further, creating an excellent internal linking structure can improve discoverability.
If the articles you give through internal links are relevant to your user, they are bound to read more content.
This reduces the bounce rates and improves the findability of your site.
Context and authority matter with regards to your internal links.
Tread carefully.
When someone clicks on a link expecting something related to the anchor text or source page but instead finds something irrelevant, it kills their user experience.
Google’s philosophy is “Do No Evil.”
The company cares about people’s experiences on your site.
A poor user experience, evidenced in high bounce rates, eventually leads to a lower SEO ranking.
External links
When another site connects to you, this is viewed as an external link for them.
Likewise, if you link out to another site, this is an external link for you.
External links have no direct impact on your ranking on PageRank score.
Even so, they position your website as a credible source of information.
External links help search engines like Google determine the relevance of your site for future ranking.
Indirectly, PageRank uses external links to estimate the popularity of a page.
The results are combined with relevancy metrics to inform ranking.
How to increase page rank with external links:
- Do not spam
- Keep them relevant
- Have external links open in new tab
- Link to authority sites
Google PageRank ToolBar
Things took a wrong turn in 2000 when Google released the preliminary version of Google PageRank toolbar for Internet Explorer.
The toolbar enabled the use of Google Search through Internet Explorer.
However, the toolbar also made it possible for people to see how the PageRank algorithm worked.
Without realizing it, Google had opened Pandora’s Box.

For SEO experts in the 2000s, the Toolbar was a helpful tool that made it possible to check page rank.
It provided a glimpse of PageRank’s numeric rating and formula for how they ranked pages.
However, cardsharps saw an opportunity to game the system using this tool.
They started to focus exclusively on Google PageRank as a measurement for improving rankings, driven by their new understanding of the algorithm used in SEO ranking.
Google had positioned links as the reliable votes for ranking on the web, and it backfired on them.
In the 2000s, you would wake up to random emails requesting you to link back to the site.
Sometimes people would offer money for links.
Other times, they would unscrupulously spam the comment section of your site with dozens of links to their websites.
People earned unfairly from it, not just SEO ranking but also significant sums of cold hard cash from selling links.
The link business gave rise to link farms.
These are farms that would sell links to you if you wanted to improve page ranking.
Their work was linking to your site from various pages in their link farms — a collection of hacked or fake websites.
Google banned and de-indexed some of these link farms and their clients, top among them SearchKing.
The latter sued Google, but a judge ruled in favor of Larry Page’s search engine.
The search giant banned and prohibited link farms and the practice of selling and buying links for ranking.
But that didn’t stop the booming link economy.
Following countless complaints, in 2005, Google acted by introducing no-follow tags.
This slightly helped to reduce the ability to distribute PageRank credit via links.
But it wasn’t until after the abolishment of PageRank toolbar in 2016 that link mining stopped.
In 2008, PageRank suffered a significant blow.
Google launched its Chrome browser with a built-in ability to search from the address bar.
That rendered the Toolbar useless.
Also, Google suspended Firefox support for Toolbar in 2011.
The company’s last update for PageRank was in 2013.
They would then stop supporting and updating the public-facing tool in 2014.
They faced it out entirely in 2016.
However, this doesn’t mean that Google stopped using its Google PageRank algorithm.
They simply chose to hide the way it works to curb link scammers and other black hat techniques.
PageRank, Google’s original magic scepter, has since been vaulted away.
Experts may guess around, but only Google knows how current SEO ranking works.
Link Build Your Web Page
![What role will link building have for SEO in 2020? [Updated] – Adlibweb](https://www.adlibweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/link-building.jpg)
Link building is getting hyperlinks from other sites to your site.
A link is a way for users to navigate between web pages.
Search engines depend on links to crawl the web.
They crawl links between pages on your website, and they also crawl links between different websites.
There are many ways to build links.
While varying in complexity, SEO experts acknowledge that online link building is perhaps the most challenging part of their work.
Many businesses pour time and resources into this, trying to get it right.
If you master link building, you will be unstoppable in SEO ranking.
Establishing link authority can help with brand popularity in your niche.
It will make you a thought leader.
One foolproof technique to build more links is writing high-quality, relevant content.
For instance, if you create a well-optimized article based on verifiable industry data and publish it, you improve the chances of people linking to you.
You can use BiQ Content Intelligence to enhance your success in content creation.
Content Intelligence gives you practical SEO content writing strategies.
For instance, as you type content in the block editor, you will get by-the-minute suggestions on optimizing your content.
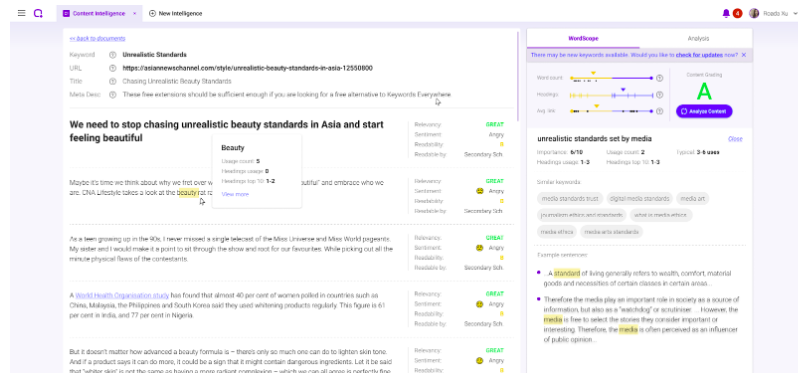
If you enter a word or phrase that has been listed in suggested keyword terms, you will see that it will be highlighted in yellow.
Content Intelligence real-time text editor offers insights on how well your text is clear, keywords that should be added, and other recommendations to help you produce A-grade content.
Wrapping It Up
Although Google PageRank’s patent has expired, the formula is still an essential centerpiece for many SEO practices today.
Understanding how it works and the factors that influence it can still help us optimize our page rankings in Google search.