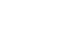Many people do not practice this but to excel in SEO, you'll need to learn the difference in HTTP status code, what they're for, and the impact it brings to your SEO.
HTTP Status Codes: What Are They, and How Do They Work?
Unfortunately, very few SEO experts know and understand how HTTPS status codes work. You’ve probably even interacted with several of these status codes without noticing.
HTTP status codes are the three-digit responses servers return whenever a client requests action on a search engine. These status codes are divided into five classes and have several variants, each of which conveys a different message.
As such, every SEO expert out there must strive to at least know some of these HTTP response codes by heart. This should enable you to evaluate any situation quickly and respond to each issue swiftly.
Our team prepared a detailed review of what HTTP status codes are, the types of HTTP status codes, and what each means for your website.
Here’s a good read:
What Are HTTP Status Codes?
These are the three-digit responses a server normally returns whenever a client makes a request on the search engine.
When you request a page on your browser, you make dozens of requests to the server, asking for specific information needed to view and render a specific web page. However, all these processes occur in a flash. So, you hardly ever notice the delay or the processes executed in the background.
That said, HTTP status codes are crucial for making it possible to connect you with your requested web page.
HTTP, an acronym for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, communicates and exchanges data between your search engine and the server.
Why Are HTTP Status Codes Important to SEO?
Generally, the goal of any SEO strategy is to drive more organic traffic to your website. Every content creator is always looking to have more visitors who are interested in what they have to say click on their websites.
However, you must ensure that your content and web page is accessible to search engine crawlers to boost your organic traffic. So, when they request to crawl through your content, they can easily access it, render it, and display it to respective searchers.
If everything is okay, the HTTP status 200 OK will be returned, which means that everything is functioning smoothly. What you don’t want on the other side of your clients’ screens are the HTTP status codes 4xx or 5xx to be returned.
Primarily, you’ll want the HTTP status code to be 3xx to a minimum.
Websites and search engine crawlers speak HTTP. Therefore, the only way you can be an effective SEO expert is to study and understand the messages they’re conveying. What’s the point of seeing these HTTP status codes every day but not understanding why they happen or how to capitalize on them or prevent them?
Classes of HTTP Status Codes
Before we dive into the different status codes, here’s a quick review of the different types, the five HTTP status code classes:
It’s worth learning the most impactful and most common status codes that your clients are likely to receive:
- 1xxs – Informational Responses
All HTTP 1xx status codes are informational. Generally, 1xxs status codes indicate that your request has been received and understood but simply hasn’t been processed yet. These requests are rarely seen, making them less relevant compared to other HTTP status codes.
- 2xxs – Successful Responses
These status codes indicate that your requests have been successful and that everything went according to plan.
While all 2xxs status codes are great, the most important status code in this category that’s worth knowing is the 200 OK status code.
- 3xxs – Redirects
These codes generally indicate to the user that further action is needed to complete a response. The request was received. However, it cannot be fulfilled.
- 4xxs – Client Errors
These status codes indicate that there’s an error on the client’s side, not the server. Some of the possible reasons for this error might be because the client isn’t authorized to request that specific web page, making too many requests, and requesting a non-existent page.
- 5xxs – Internal Server Errors
A 5xx error is served when a client makes a valid request, but the server cannot complete it for whatever reason. For instance, the website may be temporarily down for maintenance or too busy to grant the client’s request.
Types of HTTP Status Codes That Marketers Need to Know
Every professional SEO or website owner must know and understand these HTTP status codes for them to be able to respond swiftly whenever any issue arises.
Imagine you are working on a website that’s showing multiple 5xx status code errors. It will make more sense knowing off the top of your head which issue you’re dealing with. 4xx status errors affect your visitor’s experience, enabling you straight away to think about any changes you might have made to affect your URLs.
Once you understand what’s the root cause of the HTTP status code, you can start looking for the best strategies like implementing a custom 404 page or using the all-powerful 301 redirects. A 301 redirect will send your audience to the right place, thereby taking care of your status code issues.
It’s also worth learning and committing to memory the impactful status codes that may harm your web page’s organic traffic, leads, and conversions. This way, you’ll quickly identify any HTTP status code and quickly evaluate it, providing a swift solution at the end.
1. 200 OK
This is perhaps the most welcome status code on the list. For one, you never see it. Then, it means that your request was successfully received and responded to. Everything is working properly. The server will reply to the client’s request with the requested content, i.e., the web page the client requested from the search engine.
NOTE: 200 OK isn’t an error code. It simply means that everything is working smoothly as it should. It is the ideal status code for a normal, everyday, properly functioning web page. Searchers, bots, and link equity pass through such links like a dream. You can go about your day securely, knowing that everything is as it should be.
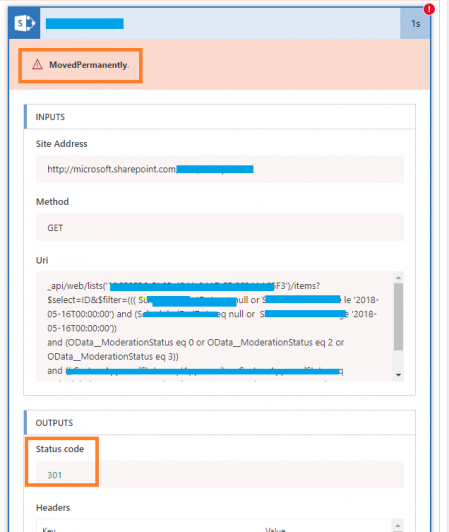
2. 301 Moved Permanently
This status code indicates that the contents of a specific web page have been permanently moved to another location. Therefore, your current request and all future requests will be redirected to the new website link instead of the source you initially requested.
Due to its permanent nature, every signal from the requested website link that’s being redirected will be passed to the new destination website link.
Another critical fact to note is that browsers will cache 301 redirects for additional requests in the future. Consequently, this will lead to a better user experience for visitors by displaying the redirected web pages faster.
Before you publish new blog posts, you’ll also want to get them checked for maximum optimization using BiQ Content Intelligence. The Content Intelligence tool ensures that all content you draft achieved semantic content intelligence for higher rankings in the SERPs.
Today, it’s more important than ever that content marketers refine their content strategies to meet the modern day’s more sophisticated search engine demands. Search engines place immense focus on delivering the highest-quality content to searchers. BiQ’s Content intelligence makes that possible by providing users with critical data centered on boosting website visibility and overall rankings.
3. 302 Moved Temporarily
The HTTP status code 302 indicates that the website URL you’re searching for has been temporarily moved to a different location.
Due to its temporary nature, no relevance or popularity signals from the redirected web page are passed to the destination website URL. Therefore, the redirected URL will still rank in the SERPs instead of being consolidated.
NOTE: When you place a 302 redirect on a website for too long, search engines may treat it as a 301 redirect, a permanent redirect.
- Using 302 Redirects Will Cause You to Lose the SEO Link Authority of the Old Page
As a content marketer, it’s always advisable that you use the 301 redirects instead of the 302 redirects when possible. That’s because, with a 302 redirect, you will lose the SEO link authority of your old web page. Search engine crawlers will treat the requested site URL as a temporary page.
4. 304 Not Modified
This status code indicates that the client’s requested resource hasn’t received any modifications since its last request. Therefore, it won’t be returned to the client. Instead, the browser will use the older cached version of the requested source.
Think of it this way. The browser performs the redirect instead of the server.
5. 400 Bad Request
This HTTP response code indicates that the server can’t or won’t process the client’s request.
This may be due to something perceived by the server to be a client error. It may be due to a malformed request syntax or deceptive request routing.
6. 401 Unauthorized
This status code indicates an error that the HTTP Authentication failed. Web pages with such HTTP status codes require either a username plus password or don’t allow certain clients access based on their IP addresses.
You’ll typically see this status code when search engine crawlers attempt to access staging environments, but you have implemented HTTP Authentication to prevent such action. Otherwise, third parties may be accessing some of your privileged information without your knowledge.
7. 404 Not Found
404 error for short. This HTTP status code indicates that the client’s requested resource could not be found. However, this doesn’t explicitly say that the requested resource could be found before.
It just says something like, “Hey, we cannot find what you are looking for (anymore).”
The 404 status code is probably one of the most common error codes regular online users come across while browsing the web since it’s the one that comes up whenever they click on a broken link.
Having this status code on your website will negatively impact your SEO and overall user experience, thereby lowering your rank in the SERPs.
8. 410 Gone
This particular status code indicates that the client’s requested website URL was permanently removed. Therefore, the URL existed before, but was explicitly removed and won’t come back.
Generally, search engines like Google are quick to remove web URLs from their index whenever the 410 error returns, making it one of the most powerful tools in any SEO toolbox. As such, ensure you harness its power with care.
9. 429 Too Many Requests
The 429 status code error is often seen as a temporary version of the 403 status code, especially when clients make too many requests within a certain timeframe. If such requests keep on coming despite the 429 error, the server may switch to start responding using the HTTP status code 403.
However, if the server continues to return the 429 code for longer periods, then Google may decide to remove the content that the clients are receiving the codes for. Always ensure you run the right status codes to allow you to respond swiftly to such errors.
10. 503 Service Unavailable
This 5xxs status code indicates that the server you’re trying to access is temporarily unavailable. It will be available later.
Often, 503 status codes are due to scheduled maintenance, or the server is just too busy to respond to your request at the moment. It allows website owners to include a “Retry-After” value, basically saying you should try again later. The server can process your request then.
11. 504 Gateway Time Out
Officially, this HTTP status code doesn’t exist. It was initiated by Cloudfire and sent to clients when their requested origins time out. Often, the issue emanates from the server that Cloudfire is using, not Cloudflare itself.
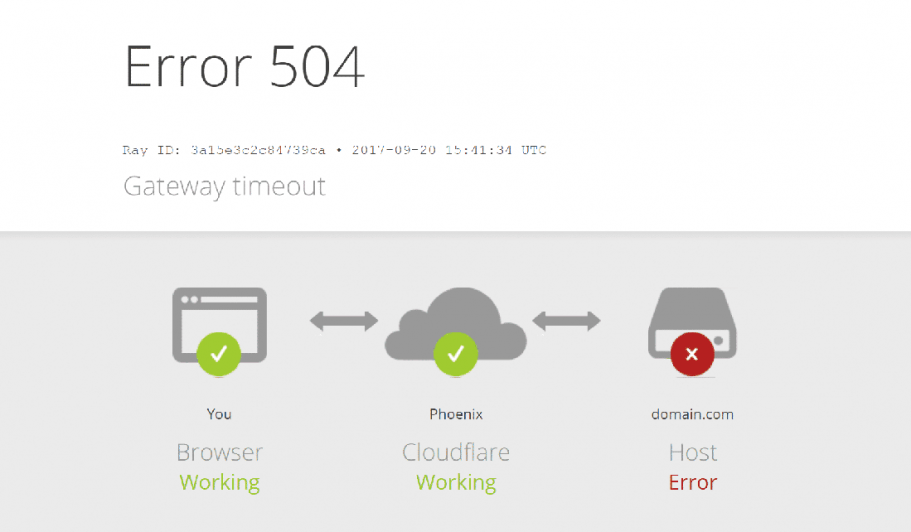
When this status code is sent, it means that the server Cloudfire is using didn’t receive the response fast enough from the other server it was making the request to. If this happens, you might have to wait a while before retrying your request again. You may have better luck then.
Make Sure There isn’t Any Faulty Https Status Code In Your Site
The above excerpt shows that HTTP status codes play a critical role in quickly sending a message across between servers and clients. Therefore, it’s important that every SEO expert knows these HTTP response codes by heart. This practice will make you much more effective in optimizing your website for your visitors and search engines.
You’ll know which issue each status code represents and know the right diagnosis and recommended solution for any issues.
It takes a lot to make your website 100% crawlable. But these HTTP status codes help make your job a lot easier down the road.